What do you do if it is raining outside and you can't fly your new copter? Of course you are using the a simulator

But the simulator which is integrated in the DJI Go smartphone app requires that you turn on the copter and it's not that great on the small screen. This was the reason I tried to use the remote control for my PC or Mac to use more professional simulators.
I have the Phantom 3 Standard, with the remote control GL358wA, which connects over WiFi to the smartphone (the remote control creates a WiFi hotspot to which the smartphone connects) instead of using an USB connection like with other DJI models. But there is still an USB port and if I connect it to my Windows PC, it gets enumerated as a serial port. Unfortunately I couldn't find any documentation how to use it, and so far no answer from the
DJI dev forum. So I tried to do something with the WiFi network.
Turns out there is an open port 2345, which sends the stick positions and I can read it with a simple Python script. With
foohid I can simulate a gamepad in Python and that's all I need to use it in a flight simulator like
Heli-X, which has a Phantom copter as a model in the free version. Now I can practice flying drones and helicopters with my Mac.
Video how I found and hacked the protocol, and how it works:
Python source code:
import socket
import foohid
import struct
joypad = (
0x05, 0x01, 0x09, 0x05, 0xa1, 0x01, 0xa1, 0x00, 0x05, 0x09, 0x19, 0x01, 0x29, 0x10,
0x15, 0x00, 0x25, 0x01, 0x95, 0x10, 0x75, 0x01, 0x81, 0x02, 0x05, 0x01, 0x09, 0x30,
0x09, 0x31, 0x09, 0x32, 0x09, 0x33, 0x15, 0x81, 0x25, 0x7f, 0x75, 0x08, 0x95, 0x04,
0x81, 0x02, 0xc0, 0xc0)
try:
foohid.destroy("FooHID simple joypad")
except:
pass
foohid.create("FooHID simple joypad", struct.pack('{0}B'.format(len(joypad)), *joypad))
s = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM)
s.connect(("192.168.1.1", 2345))
def word(b0, b1):
return (b0 << 8) | b1
def conv(w):
return (w / 8 - 128) & 0xff
while True:
data = bytearray(s.recv(1024))
# print(' '.join("%02x" % x for x in data))
if len(data) == 26:
rightX = word(data[12], data[11])
rightY = word(data[14], data[13])
leftY = word(data[16], data[15])
leftX = word(data[18], data[17])
cam = word(data[20], data[19])
foohid.send("FooHID simple joypad", struct.pack('H4B', 0,
conv(rightX), conv(rightY), conv(leftX), conv(leftY)))
print("leftX: %4i, leftY: %4i, rightX: %4i, rightY: %4i, cam: %4i" % (
leftX, leftY, rightX, rightY, cam))
I tested it on Windows with vJoy. If you have a laptop, you can connect to the Phantom remote control. On my desktop PC I used an USB WiFi dongle, like this, which you can get for less than $5 and free shipping:
https://www.amazon.com/150Mbps-802-11n-Wireless-Adapter-Network/dp/B009D8DEPSIn Windows device manager it says "Realtek RTL8188ETV Wireless LAN 802.11n USB 2.0 Network Adapter". Works in Windows 10 without additional driver installation. Then you can see the remote control with the network icon in the task bar and you can connect to it:
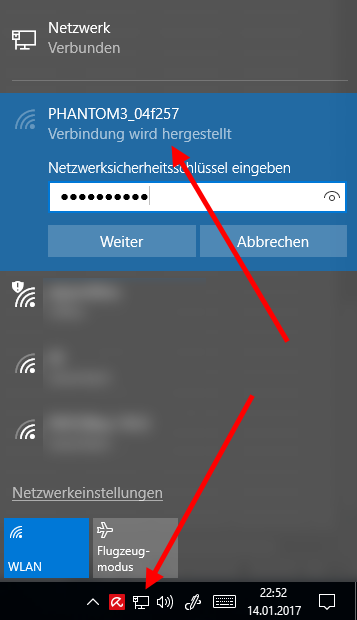
Note, you should really change the default WiFi password with the mobile phone DJI Go app.
Click "yes" to the next question Windows asks. In a DOS prompt you can check the connection with "ipconfig", it should show something like this and the numbers should change when you move the sticks:
Drahtlos-LAN-Adapter WLAN:
Verbindungsspezifisches DNS-Suffix: local
Verbindungslokale IPv6-Adresse . : xxxx::xx:xxxx:xxxx:xxxx%12
IPv4-Adresse . . . . . . . . . . : 192.168.1.20
Subnetzmaske . . . . . . . . . . : 255.255.255.0
Standardgateway . . . . . . . . . :
Note: this might not work, if your primary network adapter starts with 192.168.1.*, you have to change this first to something like 192.168.2.*.
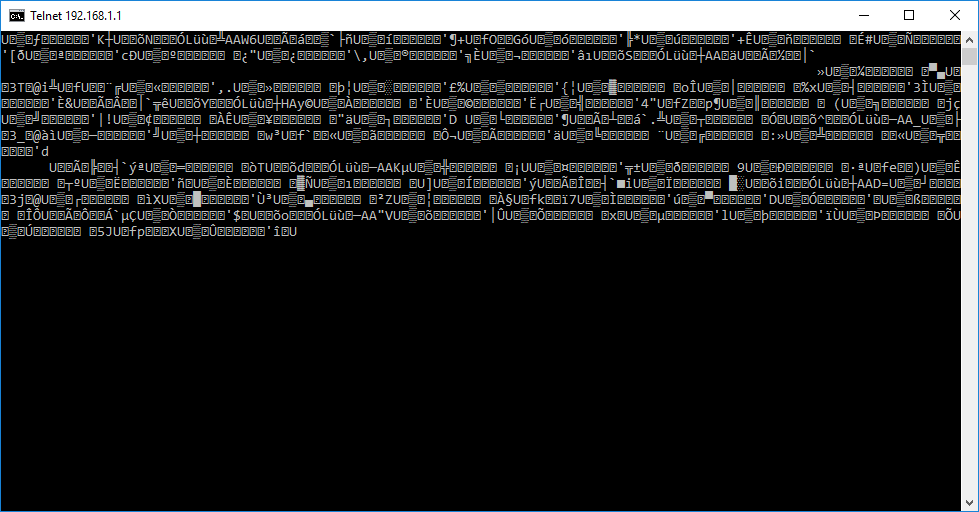
You can check if the remote sends data by "telnet 192.168.1.1 2345" from a DOS command prompt (you might need to install the telnet client first with the standard Windows applications). If this looks like this, and new garbage characters are written all the time, the connection to your remote works:
Next install Python 3. Then use this script to test if the stick positions can be read:
import socket
import struct
s = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM)
s.connect(("192.168.1.1", 2345))
def word(b0, b1):
return (b0 << 8) | b1
def conv(w):
return (w / 8 - 128) & 0xff
while True:
data = bytearray(s.recv(1024))
if len(data) == 26:
rightX = word(data[12], data[11])
rightY = word(data[14], data[13])
leftY = word(data[16], data[15])
leftX = word(data[18], data[17])
cam = word(data[20], data[19])
print("leftX: %4i, leftY: %4i, rightX: %4i, rightY: %4i, cam: %4i" % (
leftX, leftY, rightX, rightY, cam))
Save it as remote.py and start it from a DOS prompt with "python remote.py". It should show something like this:
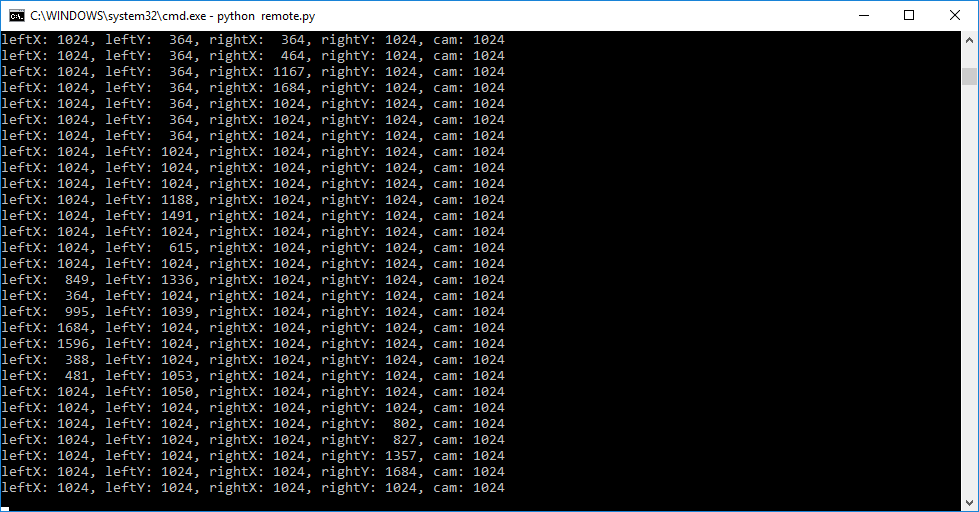
Next donwload and install the vJoySetup.exe driver, I used this version:
https://sourceforge.net/projects/vjoystick/files/Beta%202.x/2.1.8.33-110117/For using vJoy with Python, I found a forum post:
http://vjoystick.sourceforge.net/joomla256.02/index.php/forum/4-Help/1044-getting-started-with-python . It is really easy to simulate a joystick from a Python script, I added this to my remote.py program:
import socket
from ctypes import *
# init vJoy
vjoy = CDLL('C:\\Program Files\\vJoy\\x86\\vJoyInterface.dll')
vjoy.AcquireVJD(1)
vjoy.ResetVJD(1)
# connect to remote
s = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM)
s.connect(("192.168.1.1", 2345))
# some helper functions
def word(b0, b1):
return (b0 << 8) | b1
def conv(w):
return (w / 8 - 128) & 0xff
def scale(x):
return int((x - 364) / 1320 * 32768)
# read data from the remote and set the axis in vJoy
while True:
data = bytearray(s.recv(1024))
if len(data) == 26:
rightX = word(data[12], data[11])
rightY = word(data[14], data[13])
leftY = word(data[16], data[15])
leftX = word(data[18], data[17])
cam = word(data[20], data[19])
print("leftX: %4i, leftY: %4i, rightX: %4i, rightY: %4i, cam: %4i" % (
leftX, leftY, rightX, rightY, cam))
vjoy.SetAxis(scale(leftX), 1, 48)
vjoy.SetAxis(scale(leftY), 1, 49)
vjoy.SetAxis(scale(rightX), 1, 50)
vjoy.SetAxis(scale(rightY), 1, 51)
Start the script with "python remote.py" from a command prompt, and then you can use the Phantom remote control as a joystick. If you have multiple joysticks connected to your system, configure the vJoy joystick for your game, e.g. heli-x:
http://www.heli-x.info/cms/download-2/This game crashes on my system, looks like some problems with the OpenGL driver, but the joystick works. You can test it e.g. with the vJoy monitor program:
C:\Program Files\vJoy\x64\JoyMonitor.exe
Another nice quadcopter simulator is FPV Freerider:
https://fpv-freerider.itch.ioWorks with no problems in Linux with my Taranis remote, should work in Windows, too, with the vJoy driver and the Phantom remote control.